Bits and bytes are fundamental concepts in the binary system, which forms the basis of how digital computers store and process information.
1. Bits (Binary Digits):
- A bit is the smallest unit of data in a computer.
- It can have one of two possible values: 0 or 1. These represent two states, such as off/on, false/true, or low/high voltage.
- Bits are the basic building blocks for more complex data types and systems.
2. Bytes:
- A byte consists of 8 bits. It is a common unit used to represent data in computers.
- With 8 bits in a byte, there are 256 possible combinations of 0s and 1s (). This means a byte can represent values from 0 to 255 in decimal.
- Example: The binary number 10101010 is a byte and can be converted to the decimal number 170.
3. Nibbles
A nibble is similar to a byte, but has 4 bits rather than 8:
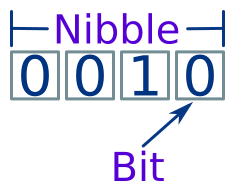
A nibble has 16 possible values, and can represent integer values from 0 to 15.

3. Binary System:
- The binary system, or base-2, is a number system that uses only two digits: 0 and 1.
- Every number in the binary system is composed of bits. In this system, values are determined by powers of 2.
- For example, in the number 1101 (binary), the value is calculated as:
- (decimal)
4. How the Binary System Works in Computers:
- Data Storage: All data in a computer, whether text, images, audio, or video, is stored as a combination of bits in binary form.
- For example, a single character in text is often stored as 1 byte (8 bits), allowing for 256 possible characters.
- Instructions: Computers operate using binary instructions, with machine language being composed of binary sequences that the CPU executes.
- Logic Operations: Logic gates in digital circuits work with binary inputs (0 or 1) and produce binary outputs, allowing computers to perform complex operations.
5. Other Data Units:
- Beyond bits and bytes, larger units of digital storage are used:
- Kilobyte (KB): 1,024 bytes (2^10 bytes).
- Megabyte (MB): 1,024 KB or bytes.
- Gigabyte (GB): 1,024 MB or bytes.
- Terabyte (TB): 1,024 GB or bytes.
- These units represent progressively larger quantities of data, from the small kilobytes used in text files to the terabytes used in hard drives.
Key Points to Remember:
- Bit: The smallest unit of data, 0 or 1.
- Byte: A group of 8 bits, commonly used to represent a single character or piece of data.
- Binary System: A number system that uses two symbols (0 and 1), essential for computer operations.
- Conversion: Binary to decimal and vice versa requires understanding powers of 2.
Summary Table:
| Unit | Size in Bits | Decimal Equivalent |
|---|---|---|
| Bit | 1 bit | 0 or 1 |
| Nibble | 4 bits | 0 to 15 |
| Byte | 8 bits | 0 to 255 |
| Kilobyte (KB) | 1,024 bytes | ~1,000 bytes |
| Megabyte (MB) | 1,024 KB | ~1,000,000 bytes |
| Gigabyte (GB) | 1,024 MB | ~1,000,000,000 bytes |
Bits and bytes are fundamental for understanding how computers process, store, and communicate data, and mastering the binary system helps make sense of how digital systems operate at a basic level.
| Telegram | Click Here |
| Instagram | Click Here |
| YouTube | Click Here |
| Mail Id | helpdesk.sharmagtech@gmail.com |
| App Link | Click Here |
User can also download the app of this website by scanning the QR code/link.
APP LINK-:: CLICK HERE



0
Post a Comment
Do leave your comments.